GINGIVITIS: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, TREATMENTS - Dr. Jigisha
What Is Gingivitis?
To put it in simple terms, gingivitis is the inflammation of the gingiva or gums. Gingivitis happens to be the most common form of gum disease. Although gingivitis is non-destructive it can progress to periodontitis, which is a more severe form of gum disease. Once periodontitis sets in, it leads to the destruction of the bone, which leads to loosening of the teeth and ultimately tooth loss. Thus, it becomes imperative to diagnose and treat gingivitis at the earliest and stop its progression.
What Causes Gingivitis?
Gingivitis can be of two forms, namely acute and chronic. Acute gingivitis has a sudden onset, lasts for a short duration, and can be painful. Whereas, chronic gingivitis sets in slowly and lasts longer, may or may not be associated with pain.
No matter the form of gingivitis, the most important and leading cause of this disease is poor oral hygiene. Poor oral hygiene leads to the accumulation of plaque on the tooth surface that is adherent to the tooth structure. This plaque is the offending substance and is composed of bacteria, salivary substances, and starch that comes from the food we eat. If plaque is not removed, it stays on teeth and eventually hardens under the gumline forming calculus, which can not be removed by brushing and requires professional cleaning. Calculus harbors disease-causing bacteria and protects them from the outside environment. These bacteria release noxious substances which acts as an irritant to the gum. The body tries to fight this infection and calls upon the protective cells, that is the inflammatory cells to destroy the bacteria. This process leads to inflammation of the gums, and gingivitis sets in. Gingivitis can further progress to a more destructive and severe form of the disease called periodontitis and it is important we treat it as soon as possible.
There are many risk factors for gingivitis other than poor oral hygiene that increases the chance of contracting the disease. These are:
- Smoking or chewing tobacco.
- Old age.
- Trauma to gums.
- Dry mouth or Xerostomia.
- Vitamin C deficiency and poor nutrition.
- Compromised immunity associated with conditions like HIV-AIDS, leukemia, cancer therapies, and diabetes.
- Anti-epileptic drugs like phenytoin, calcium channel blockers are used for heart conditions like hypertension.
- Hormonal changes occur during puberty, pregnancy, and birth control medications. Studies have shown that pregnancy is almost always associated with gingivitis and a dental consultation is effective in preventing complications.
- Certain viral and fungal infections.
What Are Symptoms of Gingivitis?
Gingivitis has several manifestations depending on the cause and duration of the disease, here are the most commonly seen symptoms of gingivitis.
- The gums appear swollen, red, and puffy.
- Pain and soreness of gums.
- Bleeding from gums, especially when brushing, flossing, and biting down on fruits, for example, seeing a tinge of blood after biting down on an apple.
- Tooth pain and sensitivity to hot and cold food and beverages.
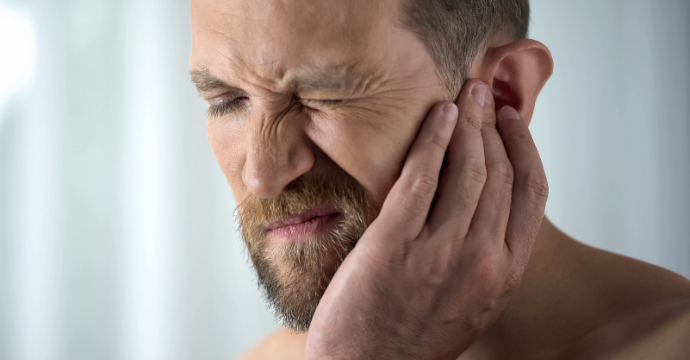
- Gingival recession, the gums lose their attachment and exposes the root surface of the tooth.
- In severe cases, where there is an additional bacterial infection like in acute necrotizing gingivitis, gums appear graying and show sloughing off. The upper layer of the gingiva gets eroded exposing the underlying structures and is very painful.
- In Desquamative gingivitis, the gums get eroded, literally shed, and appear fiery red with intense pain.
How to Treat Gingivitis?
As we have already discussed earlier, it is of prime importance that we treat gingivitis at the earliest and stop it from progressing to periodontitis where it becomes difficult to treat.
The forefront in the management and treatment of gingivitis is the maintenance of proper oral hygiene, removal of plaque, and its formation.
- Brushing regularly and properly twice a day.
- Use of interdental aids like floss and interdental brush.
- Using a mouth wash containing chlorhexidine and cetylpyridium chloride.
- Professional cleaning by a dental practitioner which removes calculus.
- Stoppage of habits such as smoking.
- Treating local causes like an improper dental filling or prosthesis.
- Treating crowding and orthodontic issues which are making maintaining good oral hygiene difficult.
- Treatment and control of systemic diseases like diabetes, AIDS, etc.
- Taking a proper diet rich in fibers.
- As per the extent of the disease, your dentist may also recommend some minor surgical procedures.
It is crucial to treat gingivitis and take care of your oral health as it affects your overall health, both physically and mentally. Schedule and dental consult at the earliest if you are facing any dental issues or experiencing any of the above symptoms.
--- By Dr. Jigisha I Graduated Bachelors in Dental Surgery from the Maharashtra University of Health Sciences, India, she is a dental surgeon from the central Indian city of Nagpur.